In most ordinary circumstances you wouldn’t dare to combine water and electricity together. In the case of hydroelectricity, however, it appears that that’s exactly what occurs… right? But, how do these complete opposing sources come together to generate one of Australia’s biggest renewable energy sources?
In this article, Canstar Blue debunks just how hydroelectricity works and where you can access it in Australia. Plus, we’ll uncover just how much of the country’s electricity generation comes from this unique clean energy source.
On this page:
- What is hydro energy?
- How is electricity generated by hydroelectricity?
- What is hydro energy used for?
- How much hydroelectricity is used in Australia?
- Can I sign up to hydro energy for my home?
- What are the advantages of hydroelectricity?
- Are there any disadvantages of hydroelectricity?
- Is hydroelectricity the best renewable energy option for Australia?
What is hydro energy?
Hydroelectricity, or hydropower, is a popular form of renewable energy that uses flowing water to generate electricity. It is a well-developed renewable energy technology that is capable of producing massive amounts of power – just as long as there is plenty of rainfall.
How is electricity generated by hydroelectricity?
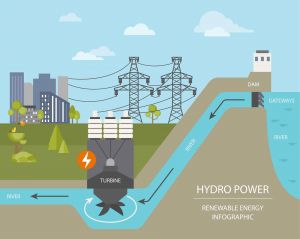
Hydroelectric generation requires a downward flow of water. The most well-known way of doing this is by constructing a dam across a river or lake that contains a gate or valve which can then control how much water flows in or out of the system. As the water flows down, it is used to push the blades of a connected turbine, which in turn generates electricity. Most hydro power stations are fitted with dozens of these turbine generators, capable of producing enough electricity to power thousands of homes and businesses.
There are three different types of hydroelectric energy plants; an impoundment facility, diversion facility and pumped-storage facility. An impoundment facility is the most common kind of plant, which uses a dam (described above). A diversion facility is similar to an impoundment facility, however instead of using a dam, it relies on a series of cannels to push flowing water towards a turbine generator.
Pumped storage facilities use a reverse effect to generate electricity, collecting energy from the sun, wind, or nuclear plants to store for later use. Through this method, water is pumped uphill until it reaches a smaller reservation pool on a higher elevation. This water is stored here until electricity is needed to be generated, in which case it is released to the bottom of the hill, where it then powers the turbines within the corresponding generators.
What is hydro energy used for?
Hydro energy is primarily used to power homes and businesses by providing a consistent renewable energy source to the grid. In addition to providing clean energy, the infrastructure used to generate hydropower can also be used for flooding control and irrigation support.
How much hydroelectricity is used in Australia?
According to the Clean Energy Council, hydroelectricity accounted for 23.3 per cent of Australia’s total clean energy supply in 2020, sitting as the third largest renewable energy supplier in the country, behind wind energy and small-scale solar. Hydropower made up 6.4 per cent of Australia’s overall electricity generation in 2020, equating to that of powering 3,184,968 homes in a year.
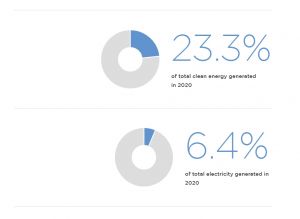
Image: Clean Energy Council, Clean Energy Australia 2021 report.
While most of Australia’s hydroelectricity is generated by Hydro Tasmania’s network of power plants and New South Wales’ Snowy Mountains Hydro Scheme, there are more than 120 working hydro power stations in the country.
Can I sign up to hydro energy for my home?
If you like what you’ve heard about hydro so far then we have some good news and bad news for you. The bad news is that it’s virtually impossible to build and install your own private hydroelectric plant to power your home. Unlike solar energy, hydroelectricity requires substantial land area – even micro plants do. So, while private hydro energy is a pipedream for now, the good news is that you can often ‘buy-in’ to hydroelectricity with your energy company.
A number of electricity providers offer to purchase power from green energy solutions on a customer’s behalf. This does not mean that household receives green energy, but the retailer pumps an agreed amount back into the grid. This is done through an initiative called ‘GreenPower’. With GreenPower, your retailer can agree to offset some or all of your energy usage by purchasing electricity from accredited renewable generators – like hydro power stations. Keep in mind, however, that some retailers may charge you extra for incorporating GreenPower into your plan.
What are the advantages of hydroelectricity?
There are quite a few advantages to using hydro power for electricity generation. These include;
- Cleaner energy source: As a renewable energy source, hydroelectricity can help to reduce carbon emissions in the energy sector.
- Flexible energy source: Hydro power stations are quite versatile and can easily interchange between higher and lower outputs of power, making them great for handling the demands of the grid, particularly in the event of a power outage or blackout.
- Supports systems beyond the grid: In addition to generating electricity, hydro plants can also aid with flood control and irrigation support. Plus, larger reservoirs can also be used for recreational opportunities in the community, such as swimming, fishing and boating.
Are there any disadvantages of hydroelectricity?

Despite the many great benefits involved with hydroelectricity, there are also some disadvantages to the clean energy source. These include;
- Relies on weather: With hydro energy relying heavily on the availability of water in order to work, in drought-stricken places or areas or extreme weather they may not be a viable option.
- Expensive to build and requires large areas: Hydro power stations carry expensive upfront costs to build. They also require significant space to be constructed and managed.
- Impacts ecosystem and wetlands: Some of the bigger reservoirs may interfere with surrounding wetland ecosystems, causing disruptions through the use of turbine gates or draining the water.
Is hydroelectricity the best renewable energy option for Australia?
Hydropower in Australia was once considered as the most significant of the ‘big three’ renewable resources – the other two being solar and wind. Though hydro has played a significant role in shaping our nation’s clean energy sources, it seems that the focus now is more towards solar and wind. This is likely due to the large upfront costs and unpredictable weather in Australia.
Despite the many benefits of hydroelectricity, constructing the required stations are a significant undertaking, not only thanks to their high upfront costs, but also with the space which is required for them to operate efficiently. Additionally, Australia’s weather patterns, particularly those seen in the summer time, may not be ideal for consistent hydropower production.
If you’re keen to start implementing more renewable energy sources into your electricity usage, be sure to check out a GreenPower or carbon neutral energy plan. Or better yet, chuck a few solar panels on your roof. Not only will you be able to generate your own, cleaner energy, but you may just find you’ll earn yourself a few dollars through your solar feed-in tariff. See which retailers Aussies reckon are ridgey-didge of solar in our annual rating below.
Image credit: Olha1981/Shutterstock.com, Clean Energy Council, Johnjen/Shutterstock.com.


Share this article