With the increasing popularity of renewable energy, more attention is being placed on the production and use of fossil fuels in Australia. While there are arguments both for and against fossil fuels, it seems many Australians are still unsure as to what they are and how we use them.
As the spotlight continues to shine on renewable energy targets and greenhouse gas emissions, it can be difficult to keep up with all the available information and to sort fact from fiction. In this article, Canstar Blue covers what you need to know about fossil fuels in Australia, including what they are, how they are used and the pros and cons of our continued reliance on them.
On this page:
What are fossil fuels and how are they formed?
Fossil fuels are hydrocarbon energy sources formed through the fossilisation of organic matter. Fossil fuels are typically made from the remains of plants and animals that have been buried and left to compound and fossilise over millions of years within the earth’s crust. Since fossil fuels are sourced from organic matter, they often have a high carbon count that makes them more harmful to the environment than other energy sources.
What are fossil fuels used for?
Fossil fuels are mainly used to generate energy in Australia. These fuels, whether they be coal, natural gas or oil, are often burned in large power stations to produce energy that is then sent to the electricity grid. In Australia, most electricity is produced in coal-fired power stations.
How are fossil fuels different to renewable fuel sources?
A key difference between fossil fuels and renewable energy sources is the level of emissions they produce. Fossil fuels, with their high hydrocarbon count, emit a large amount of carbon into the atmosphere when burned. Renewable fuel sources, like solar, wind and hydro, on the other hand, create little to no carbon emissions when generating energy, ultimately creating less pollution.
While both fossil fuels and renewable sources do occur naturally, renewable sources regenerate quicker and more efficiently than fossil fuel sources, which rely on years of decomposing remains and fossilisation to generate. As such, there is a push towards more renewable energy sources, as they are not only more sustainable for the environment, but a more readily accessible and reliable energy source.
Some renewable energy incentives already implemented in the Australian energy retail market include carbon neutral energy, GreenPower and solar panel and battery installation.
Carbon neutral energy plans in Australia
Here are some of the cheapest published deals from the retailers on our database that have a carbon offset option available. These are products from referral partners†. These costs are based on the Ausgrid network in Sydney but prices may vary depending on your circumstances. This comparison assumes general energy usage of 3900kWh/year for a residential customer on a single rate tariff. Please use our comparison tool for a specific comparison in your area. Our database may not cover all deals in your area. As always, check all details of any plan directly with the retailer before making a purchase decision. The cost of carbon neutral programs may vary from retailer to retailer.
Here are some of the cheapest published deals from the retailers on our database that have a carbon offset option available. These are products from referral partners†. These costs are based on the Citipower network in Melbourne but prices may vary depending on your circumstances. This comparison assumes general energy usage of 4000kWh/year for a residential customer on a single rate tariff. Please use our comparison tool for a specific comparison in your area. Our database may not cover all deals in your area. As always, check all details of any plan directly with the retailer before making a purchase decision. The cost of carbon neutral programs may vary from retailer to retailer.
Here are some of the cheapest published deals from the retailers on our database that have a carbon offset option available. These are products from referral partners†. These costs are based on the Energex network in Brisbane but prices may vary depending on your circumstances. This comparison assumes general energy usage of 4600kWh/year for a residential customer on a single rate tariff. Please use our comparison tool for a specific comparison in your area. Our database may not cover all deals in your area. As always, check all details of any plan directly with the retailer before making a purchase decision. The cost of carbon neutral programs may vary from retailer to retailer.
Here are some of the cheapest published deals from the retailers on our database that have a carbon offset option available. These are products from referral partners†. These costs are based on the SA Power network in Adelaide but prices may vary depending on your circumstances. This comparison assumes general energy usage of 4000kWh/year for a residential customer on a single rate tariff. Please use our comparison tool for a specific comparison in your area. Our database may not cover all deals in your area. As always, check all details of any plan directly with the retailer before making a purchase decision. The cost of carbon neutral programs may vary from retailer to retailer.
Types of fossil fuels
There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, oil and natural gas.
Coal
Coal is a carbon-heavy, solid fossil fuel that is extracted through a mining process. There are two main types of coal mining processes: underground, which uses machinery to cut into deep reservoirs to extract the coal, and surface mining, which strips back layers of dirt, soil and rock to reach the coal. In 2022, the Australian government reported that 47% of Australia’s energy generation was from coal.
Oil
Also known as crude oil or petroleum, oil is a liquid fossil fuel mostly found in underground reservoirs. Made up of hydrocarbons, oil is sourced through the process of drilling into land or sea. This fossil fuel is then transported via trains, trucks or pipelines to refineries where it is used to create gasoline, propane, kerosene and fuel. In 2022, the Australian government published that two per cent of Australia’s energy generation came from oil.
Natural gas
Natural gas, also known as LNG in Australia, is an odourless and colourless energy source made up of methane and a mix of combustible hydrocarbon gases. Like coal and oil, natural gas is sourced from underground reservoirs, where it has formed between layers of stone and rock. Natural gas is accessed through a drilling process and is transported to homes and businesses via a gas pipeline known more commonly as the gas mains. In 2022, the Australian government found that natural gas accounted for 19 per cent of energy consumption in Australia.
Related articles:
Disadvantages of fossil fuels
Over the years, research has uncovered the disadvantages of fossil fuels. While most of these have to do with the environmental impacts of fossil fuels, there are some other notable disadvantages to using fossil fuels:
- Harmful to the environment: fossil fuels release large amounts of carbon and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere when they are burned to generate energy. According to CSIRO, Australia emitted 465.2 million tonnes of carbon between June 2022 and June 2023. Electricity generation contributed to 32.6 per cent of that figure.
- Difficult to regenerate: although they do occur naturally, fossil fuels aren’t as easily regenerated as renewable energy sources due to the fossilisation required to produce them. This process can take hundreds of thousands of years, which paired with our quick consumption of these fuels, could lead to shortages in the distant future.
- Dangerous to burn: fossil fuels need to be burned in order to generate electricity and as such, are highly flammable energy sources. Not only are they environmentally harmful when burned, they are also risky to source through underground mining. Gas leaks during refinement are also extremely harmful to both the environment and the humans.
Advantages of fossil fuels
While there are quite a few environmental and supply related disadvantages to using fossil fuels, there are still some advantages to using them too:
- Easy to transport: fossil fuels don’t require any in-depth mechanical storing solutions. They can easily be transported through means that are already available to us, like pipelines, trunks and tanks.
- Well developed: we have been using fossil fuel for energy generation for years, and as such, have developed an effective, cheap and easy way to source, generate and distribute this energy source. However, as infrastructure and technology advances, renewable energy production is becoming an affordable alternative.
What does Australia’s fossil fuels use look like?
According to the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water, fossil fuels accounted for about 68 per cent of Australia’s electricity generation in 2022. Coal use in Australia dipped 4% in 2021-22, and its downward trend is shown in the graph below:
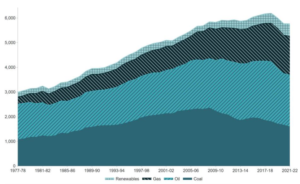
Image source: DCCEEW (2023) Australian Energy Statistics, Table C via the Australian government’s Australian Energy Update 2023 report
What does the future look like for fossil fuels?
It’s hard to determine whether or not fossil fuels will ever truly get the sack in Australia. While they are more harmful to the environment, they still remain a cheap and reliable energy source. And, despite Australia hitting its 2020 renewable energy generation target, the switch to renewable energy still remains a heated political talking point.
Switching to completely renewable sources may be a costly matter but Australia has committed to transitioning to a more sustainable and less carbon-intensive energy system in the coming years, which will ultimately be better for our planet and hopefully our hip pocket.
Original reporting by Kelseigh Wrigley
Image Source: Jag_cz/Shutterstock.com, Australian Government Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources website


Share this article